Database Access¶
Configuring Access¶
In Model Options → Databases, click Add Database to give your Assistant Model structured access to your data.
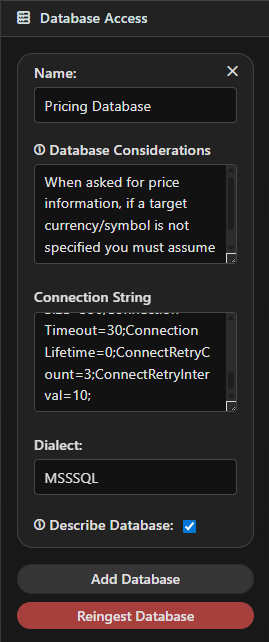
Options Explained¶
- Name – A friendly label (e.g., “Sales Warehouse”).
- Connection String – Defines how Assistant Engine connects (server, database, credentials).
Your database administrator can supply this. - Dialect – The database type (e.g., SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL).
- Describe Database – If enabled, Assistant Engine uses the Descriptor Model to generate summaries of your schema before ingestion.
This improves semantic search and SQL generation accuracy.
Database Considerations¶
- Permissions – Ensure the user account in your connection string has read access at minimum.
- Schema Size – Large schemas may take longer to ingest and vectorize.
- Updates – Re-ingest whenever your schema changes to keep knowledge up to date.
- Security – Store credentials securely; never commit them to source control or share in plaintext.
Best practice
After adding a database:
1. Test Connection to confirm credentials and connectivity.
2. Run Ingest to build the vector store.
3. Re-ingest if your schema changes.
Built-In Database Features¶
Once configured, Assistant Engine provides several database-aware tools:
- ExecuteSQL – Run direct SQL queries by asking the Assistant in natural language.
- Search Schema – Retrieve tables, columns, and relationships from your ingested schema.
- Search Database – Perform semantic search across stored schema data for context-aware answers.
When to use ExecuteSQL
Use this feature carefully — the Assistant will execute queries directly against your database.
Best suited for read-only accounts or sandbox environments to avoid accidental data changes.